John DiTusa
Professor of Physics, Department Chair
Ph.D., 1992 - Cornell University
Louisiana State University
Department of Physics & Astronomy
202K-1 and 211-B Nicholson Hall, Tower Dr.
Baton Rouge, LA 70803-4001
225-578-1195 (Chair's office) 225-578-2606-Office, 9105-Lab
ditusa@phys.lsu.edu
Research Group
Graduate Students:
 Ramakanta Chapai (rchapa3@lsu.edu)
Ramakanta Chapai (rchapa3@lsu.edu)
Co-Advisor: Rongying Jin
Postdocs:
 Sunil Karna (karna1@lsu.edu)
Sunil Karna (karna1@lsu.edu)

Yu Li (yuli1@lsu.edu)
Former Students:
Former Postdocs:
Recent Former Undergraduate Students (Over 30 have performed research in DiTusa Laboratory):
Paul Chery (REU 2016 from Macalester College)
Holden Hoyer (REU 2015 from New Mexico Institute of Mining and Technology)
Daniel Lauriola (REU 2014) from Rose Hulman Institute of Technology
Joshua Mendez (BS 2013) Florida State University
Noah Davis (BS 2013) Louisiana State University
Dominique Geatreau (BS 2013) University of Minnesota
Evan Plunkett (REU 2013 from Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute)
Kisa Valenti (BS 2012) Louisiana State University
Dylan Liu (REU 2010 from Cornell University)
Topological Spin Textures and Spin Density Wave Materials
Itinerant magnetic materials can display a wide range of interesting magnetic structures and phase transitions between different types of magnetic order. In particular, there are systems that display nanometer sized spin textures that are thought to be useful for magnetic storage applications. This research direction includes exploration of these materials to develop a fundamental understanding of the properties that drive such unusual behaviors and to search for materials that display these novel magnetic orderings.
- C. Dhital, L. DeBeer-Schmitt, D. P. Young, & J. F. DiTusa, "Unpinning the skyrmion lattice in MnSi: Effect of substitutional disorder", Phys. Rev. B 99, 024428 (2019). Article
- C. Dhital, L. DeBeer-Schmitt, Q. Zhang, W. Xie, D. P. Young, & J. F. DiTusa, “Exploring the origins of the Dzyalloshinski-Moriya interaction in MnSi”, Phys. Rev. B 96, 214425 (2017). Article
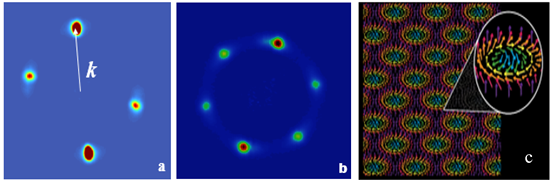
- C. Dhital, M.A. Khan, M. Saghayezhian, W. A. Phelan, D. P. Young, R. Y. Jin, & J. F. DiTusa, "Effect of negative chemical pressure on the prototypical itinerant magnet MnSi", Phys. Rev. B 95, 024407 (2017). Article
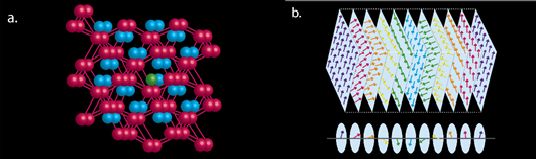
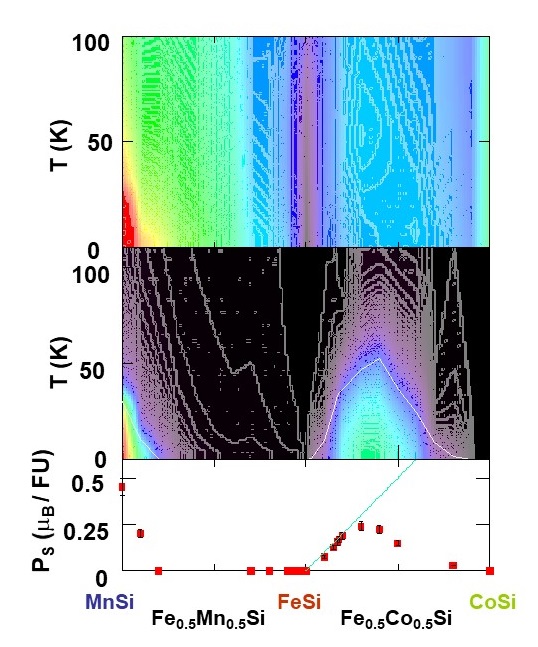
- Y. Wu, Z. Ning, H. B. Cao, G. Cao, S. Karna, K. A. Benavides, G. T. McCandless, R. Jin, J. Y. Chan, W. A. Shelton, & J. F. DiTusa, “Spin density wave instability in a ferromagnet”, Scientific Reports 8, 5225 (2018). Article
-
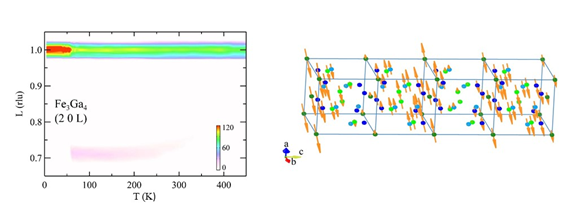
J. H. Mendez, C. E. Ekuma, Y. Wu, B. Fulfer, J. C. Prestigiacomo, M. Jarrell, J. Moreno, W. A. Shelton, D. P. Young, P. W. Adams, A. Karki, R. Jin, J. Y. Chan, & J. F. DiTusa, “Competing magnetic states, disorder, and magnetic character of Fe3Ga4”, Phys. Rev. B 91, 144409 (2015). Article
-
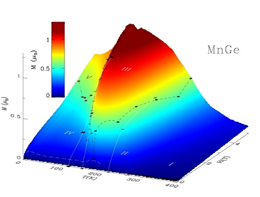
J. F. DiTusa, S. B. Zhang, K. Yamaura, Y. Xiong, J. C. Prestigiacomo, B. W. Fuller, P. W. Adams, M. I. Brickson, D. A. Browne, C. Capan, Z. Fisk, & J. Y. Chan, “Magnetic, thermodynamic, and electrical transport properties of the noncentrosymmetric B20 germanides MnGe and CoGe”, Phys. Rev. B 90,144404 (2014). Article
Magnetic Weyl Semimetals and Dirac Systems
Materials that display relativistic-like energy/momentum relations have attracted enormous recent interest in condensed matter physics for both fundamental and possible applications reasons. Our research focuses on identifying materials that display these types of behaviors, and to explore their consequences on the physical properties of materials.
-
J. Y. Liu, J. Hu, Q. Zhang, D. Graf, H. B. Cao, S. M. A. Radmanesh, D. J. Adams, Y. L. Zhu, G. F. Cheng, X. Liu, W. A. Phelan, J. Wei, M. Jaime, F. Balakirev, D. A. Tennant, J. F. DiTusa, I. Chiorescu, L. Spinu, & Z. Q. Mao, “A magnetic topological semimetal Sr1−yMn1−zSb2 (y, z < 0.1)”, Nature Materials 16, 905-910 (2017). Article
- G. Cao, W. Xie, W. A. Phelan, J. F. DiTusa, & R. Jin, "Electrical anisotropy and coexistence of structural transitions and superconductivity in IrTe2", Phys. Rev. B 95, 035148 (2017). Article
Magnetic Semiconductors and Griffiths Phases
Materials that are on the verge of insulator-to-metal and paramagnetic-to-ferromagnetic or antiferromagnetic transitions are fascinating because of the effect of the nascent ordering on physical properties. We have demonstrated that the combination of critical behaviors can lead to unusual behavior and interesting physics. This includes our work on small gap semiconductors where chemical substitution can lead to metallic and magnetic states. We have discovered that the usual behavior of carrier-doped semiconductors can be amplified by the large magnetization that external fields can produce in these systems. In addition, charge carrier screening of substitution induced magnetic moments can lead to novel non-Fermi liquid behavior in these same systems. Finally, in materials where chemical substitution can lead to ferromagnetic ordering, Griffiths phases--rare regions of nascent magnetic order--can dominate the magnetic and charge carrier properties leading to unusual behaviors.
-
J. F. DiTusa, “Silicon based Magnetic Semiconductors”, Chapter in the Handbook of Spintronics, edited by Yongbing Xu, David D. Awschalom, and Junsaku Nitta, Springer Reference (Dordrecht Heidelberg New York London) (2015).
-
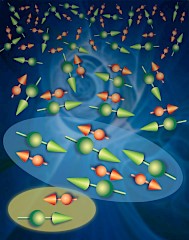
Figure 1. Image describes quantum critical physics of spin systems with temperature decreasing in the foreground. The green oval represents unpaired spin complexes responsible for the inelastic scattering which causes the non-Fermi liquid behavior.
S. Guo, D. P. Young, R. T. Macaluso, D. A. Browne, N. L. Henderson, J. Y. Chan, L. L. Henry, & J. F. DiTusa, “Magnetic and thermodynamic properties of cobalt doped iron pyrite: Griffiths phase in a magnetic semiconductor”, Phys. Rev. B 81, 144423 (2010). Article
-
S. Guo, D. P. Young, R. T. Macaluso, D. A. Browne, N. L. Henderson, J. Y. Chan, L. L. Henry, & J. F. DiTusa, “Charge transport in cobalt-doped iron pyrite”, Phys. Rev. B 81, 144424 (2010). Article
-
N. Manyala, B.D. Ngom, A.C. Beye, R. Bucher, M. Maaza, A. Strydom, A. Forbes, A.T.C. Johnson, & J. F. DiTusa, “Structural and magnetic properties of ε-Fe1−xCoxSi thin films deposited via pulsed laser deposition”, Appl. Phys. Lett. 94, 232503 (2009). Article
-
N. Manyala, J. F. DiTusa, G. Aeppli, & A. P. Ramirez, "Doping a semiconductor to create an unconventional metal," Nature 454, 976-980 (2008). Article
-
S. Guo, D. P. Young, R. T. Macaluso, D. A. Browne, N. L. Henderson, J. Y. Chan, L. L. Henry, & J. F. DiTusa, "Discovery of the Griffiths phase in the itinerant magnetic semiconductor Fe1-xCoxS2," Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 017209 (2008). Article
-
F. P. Mena, J. F. DiTusa, D. van der Marel, G. Aeppli, D. P. Young, A. Damascelli, & J. A. Mydosh, “Suppressed reflectivity due to spin-controlled localization in a magnetic semiconductor”, Phys. Rev. B. 73, 085205 1-7 (2006). Article
-
N. Manyala, Y. Sidis, J. F. DiTusa, G. Aeppli, D. P. Young, & Z. Fisk, “Large anomalous Hall effect in a silicon-based magnetic semiconductor”, Nature Materials 3, 255-262 (2004). Article
-
N. Manyala, Y. Sidis, J. F. DiTusa, G. Aeppli, D. P. Young, & Z. Fisk, ”Magnetoresistance from quantum interference effects in ferromagnets”, Nature 404, 581-584 (2000); and 408, 616 (2000). Article
-
G. Aeppli & J. F. DiTusa, ”Undoped and doped FeSi or how to make a heavy fermion metal with three of the most common elements”, Materials Science and Engineering B63, 119-124 (1999). Article
-
J. F. DiTusa, K. Friemelt, E. Bucher, G. Aeppli, & A. P. Ramirez, ”Heavy fermion metal–Kondo insulator transition in FeSi1−xAlx”, Phys. Rev. B 58, 10288-10301 (1998). Article
-
J. F. DiTusa, K. Friemelt, E. Bucher, G. Aeppli, & A. P. Ramirez, ”Metal-Insulator Transition in the Kondo Insulator FeSi and Classic Semiconductors Are Similar”, Phys. Rev. Lett. 78, 2831-2834 (1997); and 78, 4309 (1997). Article
-
K. Friemelt, J.F. DiTusa, E. Bucher, & G. Aeppli, “Coulomb interactions in Al doped FeSi at low temperatures”, Annalen der Physik 5, 175-183 (1996). Article
-
Z. Schlesinger, Z. Fisk, Hai-Tao Zhang, M. B. Maple, J. F. DiTusa, & G. Aeppli, “Unconventional charge gap formation in FeSi”, Phys. Rev. Lett. 71, 1748-17501 (1993). Article
Quantum Critical Behavior
 We make use of the ability to tune condensed matter systems so that they are in proximity
to a zero-temperature phase transition to explore quantum critical behavior. Here,
the quantum fluctuations dominate the thermal fluctuations leading to unusual behaviors
including unconventional superconductivity.
We make use of the ability to tune condensed matter systems so that they are in proximity
to a zero-temperature phase transition to explore quantum critical behavior. Here,
the quantum fluctuations dominate the thermal fluctuations leading to unusual behaviors
including unconventional superconductivity.
-
R. G. Goodrich, C. Capan, A. D. Bianchi, Z. Fisk, J. F. DiTusa, I. Vekhter, D. P. Young, L. Balicas, Y-J. Yo, T. Murphy, J. Y. Cho, & J. Y. Chan, “SC-to-AFM transition in CeCo(In1−xCdx)5: de Haas-van Alphen measurements”, J. Phys: Conf. Ser. 273, 012113 (2011). Article
-
C. Capan, Y. J. Jo, L. Balicas, R. G. Goodrich, J. F. DiTusa, I. Vekhter, T. P. Murphy, A. D. Bianchi, L. D. Pham, J. Y. Cho, J. Y. Chan, D. P. Young, & Z. Fisk, "Fermi surface evolution through a heavy fermion superconductor-to-antiferromagnet transition: de Haas-van Alphen effect in Cd substituted CeCoIn5," Phys. Rev. B 82, 035112 (2010) [Editors’ suggestion]. Article
-
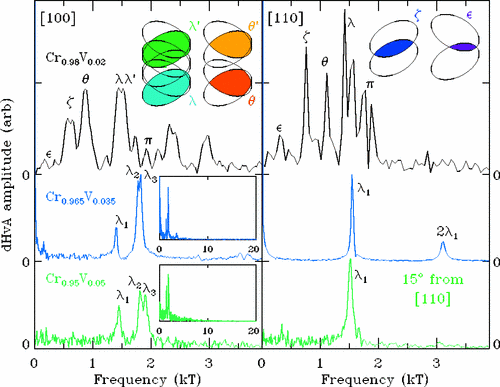
J. F. DiTusa, R. G. Goodrich, N. Harrison, & E. S. Choi, "Fermi surface of Cr1-xVx across the quantum critical point," Phys. Rev. B 82, 075114 (2010). Article
-
C. Capan, L. Balicas, T.P. Murphy, E.C. Palm, R. Movshovich,D. Hall, S.W. Tozer, M.F. Hundley, E.D. Bauer, J.D. Thompson, J. L. Sarrao, J. F. DiTusa, R. G. Goodrich, & Z. Fisk, “Unusual metamagnetism in CeIrIn5”, Phys. Rev. B 80, 094518 (2009). Article
-
C. Capan, R. G. Goodrich, J. F. DiTusa, L. Balicas, Y. J. Jo, T. P. Murphy, E. C. Palm, R. Movshovich, E. D. Bauer, M. F. Hundley, J. D. Thompson, J. L. Sarrao, D. Hall, & S. W. Tozer, “Metamagnetism in CeIrIn5: Magnetoresistance and dHvA investigation”, Physica B - Condensed Matter 403, 797-799 (2008). Article
-
 C. Capan, S. Singh, S. Wirth, M. Nicklas, H. Lee, Z. Fisk, J. F. DiTusa, & F. Steglich,
“New hints on the origin of quantum criticality in CeCoIn5: A Hall effect study”, Physica B 403 1290-1292 (2008). Article
C. Capan, S. Singh, S. Wirth, M. Nicklas, H. Lee, Z. Fisk, J. F. DiTusa, & F. Steglich,
“New hints on the origin of quantum criticality in CeCoIn5: A Hall effect study”, Physica B 403 1290-1292 (2008). Article -
C. Capan, S. Singh, S. Nair, M. Nicklas, H. Lee, J. F. DiTusa, Z. Fisk, S. Wirth, & F. Steglich, “Crossover from Landau Fermi liquid to non-Fermi liquid behavior: Indications from Hall measurements on CeCoIn5”, Physica C 460 678-679 (2007). Article
-
S. Singh, C. Capan, M. Nicklas, M. Rams, A. Gladun, H. Lee, J. F. DiTusa, Z. Fisk, F. Steglich, & S. Wirth, “Probing the quantum critical behavior of CeCoIn5 via Hall effect measurements”, Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 57001 1-4 (2007). Article
-
B. Bucher, Z. Schlesinger, D. Mandrus, Z. Fisk, J. Sarrao, J. F. DiTusa, C. S. Ogelsby, G. Aeppli, & E. Bucher, “Charge Dynamics of Ce Based Compounds: Connection between the Mixed Valent and Kondo Insulator States”, Phys. Rev. B 53, R2948-R2951 (1996). Article
-
Z. Fisk, J. L. Sarrao, J. D. Thompson, D. Mandrus, M. F. Hundley, A. Miglori, B. Bucher, Z. Schlesinger, G. Aeppli, E. Bucher, J. F. DiTusa, C. S. Ogelsby, H-R. Ott, P. C. Canfield, & S. E. Brown, “Kondo Insulators”, Physica B 206 & 207, 798-803 (1995). Article
-
G. Aeppli, Z. Fisk, & J. F. DiTusa, “Are Kondo Insulators Simply Insulators?”, Proceedings of the Los Alamos Workshop on Strongly Correlated Fermi Systems”, Springer–Verlag, New York (1994).
Superconductivity
We have discovered unconventional superconducting states in materials that are highly layered, nearly two-dimensional and in materials that have non-centrosymmetric crystal structures.
-
 M. A. Khan, D. E. Graf, D. Browne, I. Vekhter, J. F. DiTusa, W. Adam Phelan, & D.
P. Young, “Quantum oscillations and a non-trivial Berry phase in the noncentrosymmetric
topological superconductor candidate BiPd”, Phys. Rev. B 99, 020507 (2019). Article
M. A. Khan, D. E. Graf, D. Browne, I. Vekhter, J. F. DiTusa, W. Adam Phelan, & D.
P. Young, “Quantum oscillations and a non-trivial Berry phase in the noncentrosymmetric
topological superconductor candidate BiPd”, Phys. Rev. B 99, 020507 (2019). Article -
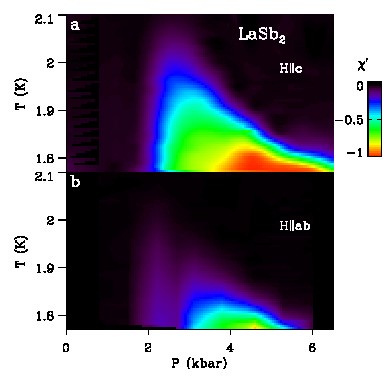
S. Guo, D. P. Young, P. W. Adams, X. S. Wu, J. Y. Chan, & J. F. DiTusa, "Dimensional crossover in the electrical and magnetic properties of the layered LaSb2 superconductor under pressure: The role of phase fluctuations", Phys. Rev. B 83, 174520 (2011).
-
J. F. DiTusa, V. Guritanu, S. Guo, D. P. Young, P. W. Adams, R. G. Goodrich, J. Y. Chan, & D. van der Marel, “Optical conductivity and superconductivity in LaSb2”, J. Phys: Conf. Ser. 273, 012151 (2011).
-
J. Y. Chan, F. R. Fronczek, D. P. Young, J. F. DiTusa, & P. W. Adams, "Synthesis, Structure, and Superconductivity in Be1.09B3"J. Sol. St. Chem. 163, 385-389 (2002).
Mechanisms for Magnetoresistance
Unusually large, linear in field, magnetoresistance was discovered in highly layered LaSb2 whose origins are as of yet unexplained. We have explored the electronic structure and high magnetic field behaviors of the compound to discover its origins.
-
 R. G. Goodrich, D. Browne, R. Kurtz, D. P. Young, J. F. DiTusa, P. W. Adams, & D.
Hall, “De Haas - van Alphen measurements of the electronic structure of LaSb2”, Phys. Rev. B 69, 125114 1-4 (2004).
R. G. Goodrich, D. Browne, R. Kurtz, D. P. Young, J. F. DiTusa, P. W. Adams, & D.
Hall, “De Haas - van Alphen measurements of the electronic structure of LaSb2”, Phys. Rev. B 69, 125114 1-4 (2004). -
D. P. Young, R. G. Goodrich, J. F. DiTusa, S. Guo, & P. W. Adams, “High magnetic field sensor using LaSb2”, Appl. Phys. Lett. 82, 3713-3715 (2003).
-
V. Yu. Butko, J. F. DiTusa, & P. W. Adams, “Tenfold Magnetoconductance in a Nonmagnetic Metal Film”, Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 162-165 (2000).
-
V. Yu. Butko, J. F. DiTusa, & P. W. Adams, ”Coulomb gap: How a Metal Film Becomes an Insulator”, Phys. Rev. Lett. 84, 1543-1546 (2000).
-
K. Lane, J. F. DiTusa, M. Park, M. S. Isaacson, & J. M. Parpia, “Electron Heating Experiments Below the Spin Glass Resistance Maximum”, J. Low Temp. Phys. 93, 7-14 (1993).
-
J. F. DiTusa, J. M. Parpia, & J. M. Phillips, “Quantum Transport in Ultrathin CoSi2 Epitaxial Films”, Appl. Phys. Lett. 57, 452-454 (1990).
-
J. F. DiTusa, J. M. Parpia, & J. M. Phillips, “Low Temperature Transport in Epitaxial CoSi2 Films”, Physica B 165 & 166, 863-864 (1990).
Quantum Spin Systems
Insulating, low dimensional spin systems are of great interest because of their inherent quantum response. We have investigated one such system where effectively one-dimensional spin chains with S=1 Ni2+ ions can be controlled through chemical substitution. This has allowed us to investigate the effect of both reducing the chain lengths and creating a large population of chain-end excitations and in creating hole carriers. Informative inelastic neutron scattering experiments were carried out to explore the changes to the excitation spectrum caused by these disruptions to the Haldane ground state.
-
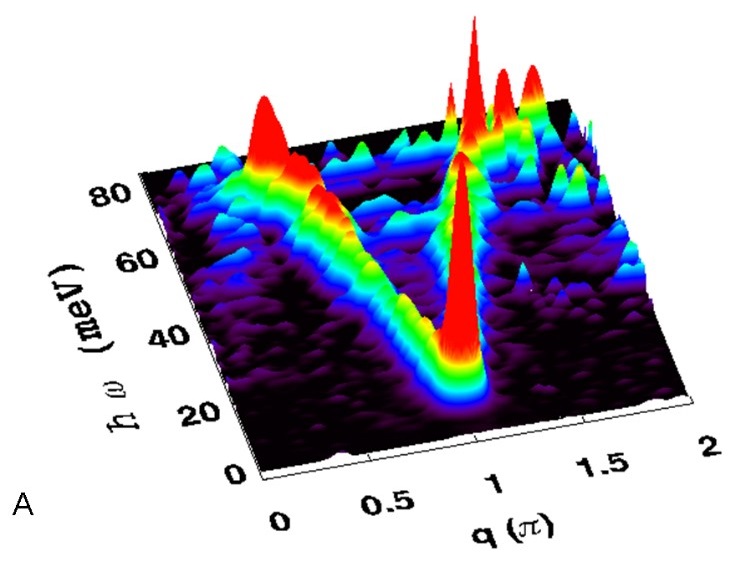 G. Y. Xu, C. Broholm, Y. A. Soh, G. Aeppli, J. F. DiTusa, Y. Chen, M. Kenzelmann,
C.D. Frost, T. Ito, K. Oka, & H. Takagi, “Mesoscopic phase voherence in a quantum
spin fluid”, Science 317, 1049-1052 (2007).
G. Y. Xu, C. Broholm, Y. A. Soh, G. Aeppli, J. F. DiTusa, Y. Chen, M. Kenzelmann,
C.D. Frost, T. Ito, K. Oka, & H. Takagi, “Mesoscopic phase voherence in a quantum
spin fluid”, Science 317, 1049-1052 (2007). -
M. Kenzelmann, G. Xu, I. A. Zaliznyak, C. Broholm, J. F. DiTusa, G. Aeppli, T. Ito, K. Oka, & H. Takagi, “Structure of end states for a Haldane spin chain”, Phys. Rev. Lett. 90, 087202 1-4 (2003); and 90, 109902.
-
G. Xu, G. Aeppli, M. E. Bisher, C. Broholm, J. F. DiTusa, C. D. Frost, T. Ito, K. Oka, R. L. Paul, H. Takagi, & M. M. J. Treacy, “Holes in a Quantum Spin Liquid”, Science 289, 419-422 (2000).
-
G. Aeppli, C. Broholm, J. F. DiTusa, S. M. Hayden, S. H. Lee, T. E. Mason, H. A. Mook, K. Oka, T. G. Perring, A. Schroder, H. Takagi, & G. Xu, ”Magnetic Coherence in the Transition Metal Oxides”, Physica B 237, 30-35 (1997).
-
G. Xu, J. F. DiTusa, T. Ito, K. Oka, H. Takagi, C. Broholm, & G. Aeppli, “Y2BaNiO5: A Nearly Ideal Realization of the S=1 Heisenberg Chain with Antiferromagnetic Interactions”, Phys. Rev. B 54, R6827-R6830 (1996).
-
C. Broholm, G. Aeppli, S.-H. Lee, W. Bao, & J. F. DiTusa, “Strong Magnetic Fluctuations in Transition Metal Oxides”, J. Appl. Phys. 79, 5023-5028 (1996).
-
G. Aeppli, W. Bao, C. Broholm, S.-W. Cheong, P. Dai, S. M. Hayden, T. E. Mason, H. A. Mook, T. G. Perring, & J. F. DiTusa, “Magnetic Correlations in Doped Transition–Metal Oxides”, Spectroscopy of Mott Insulators and Correlated Metals, Springer Series in Solid State Sciences, 119, Edited by A. Fujimori and Y. Tokura, Springer Verlag, Berlin, 205-212 (1995).
-
J. F. DiTusa, S-W. Cheong, J.-H. Park, G. Aeppli, C. Broholm, & C. T. Chen, “Magnetic and Charge Dynamics in a Doped One–Dimensional Transition Metal Oxide”, Phys. Rev. Lett. 73, 1857-1860 (1994).
Other Publications
-
M. Li, S. L. De Rooy, D. K. Bwambok, B. El-Zahab, J. F. DiTusa, & I.M.Warner, “Magnetic chiral liquids derived from amino acids”, Chem. Comm. 45, 6922-6924 (2009).
-
J. F. DiTusa, K. Lin, M. S. Isaacson, & J. M. Parpia, “Role of Phonon Dimensionality on Electron–Phonon Scattering Rates”, Phys. Rev. Lett. 68, 1156-1159 (1992).
-
J. F. DiTusa, K. Lin, M. Park, M. S. Isaacson, & J. M. Parpia, “Finite–Size Effects in the Low–Temperature Resistivity of CuCr Films”, Phys. Rev. Lett. 68, 678-681 (1992).
-
J. F. DiTusa, Y. K. Kwong, K. Lin, M. Park, M. S. Isaacson, & J. M. Parpia, “The Electron–Phonon Scattering Rate in Thin Free–Standing Metallic Films”, Proceedings of the Seventh International Conference on Phonon Scattering in Condensed Matter, 143-144 Springer–Verlag, New York (1992).
-
V. Kotsubo, J. F. DiTusa, T. Hall, R. Mihailovich, & J. M. Parpia, “Reduction of the Superfluid Fraction of 3He in Sintered Silver”, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 26 143-144 (1987).
-
R. E. Warner, J. F. DiTusa, A. Nadasen et al. “The Mechanism of the 7Li(d,2α)n Reaction From Ed = 3 to 15 MeV”, Nuclear Physics A470, 339-348 (1987).